How To Choose the Tool Geometry Parameters of CNC Cutting Stainless Steel?
Tool rake angle g0: The hardness and strength of stainless steel are not high, but the plasticity and toughness are good, the heat strength is high, and the chips are not easily cut off during cutting. Under the premise of ensuring that the knife has sufficient strength, a larger rake angle should be used. This not only reduces the plastic deformation of the metal to be cut, but also reduces the cutting force and the cutting temperature while reducing the depth of the hardened layer.
The front angle of turning various stainless steels is approximately 12° to 30°. For martensitic stainless steel (such as 2Cr13), the rake angle can take a larger value; For austenitic and austenitic + ferritic stainless steels, the rake angle should be a small value; For stainless steels with low hardness after quenching and tempering or quenching and tempering, a larger rake angle may be adopted; For smaller diameter or thin-walled workpieces, a larger rake angle should be used.
High-speed steel milling cutter takes gn=10°~20°, and cemented carbide milling cutter takes gn=5°~10°; The reamer generally takes g0=8°~12°; the tap generally takes g0=15°~20° (machine) or g0=20° (hand).
Back angle a0: Increasing the relief angle reduces the friction between the flank and the machined surface, but reduces the strength and heat dissipation of the cutting edge. The reasonable value of the back angle depends on the cutting thickness, and the cutting thickness is small, and a larger relief angle should be selected.
Stainless steel turning tools or boring tools usually take a0=10°~20° (finishing) or a0=6°~10° (roughing); The high speed steel end mill takes a0=10°~20°, and the end mill takes a0=15°~20°; The hardness alloy end mill takes a0=5°~10°, and the end mill takes a0=12°~16°; The reamer and the tap take a0=8°~12°.
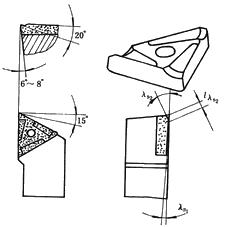
figure 1. Double edge angle chip breaking lathe tool
The main declination Kr, the auxiliary deflection angle K 'R, and re:
Reducing the tool's leading angle can increase the working length of the blade, which is good for heat dissipation. However, the radial force is increased during the cutting process, and vibration is easily generated, often taking kr=45°-75°. If the rigidity of the machine is insufficient, it can be increased appropriately. The secondary declination is usually taken as k'r = 8° to 15°. In order to strengthen the cutting edge, the cutting edge arc of e=0.5~1.0 mm should generally be ground.
Blade inclination ls:
In order to increase the strength of the tool tip, the inclination angle of the cutting edge is generally ls=-8° to -3°, and the larger value ls=-15° to -5° in the intermittent cutting.
In the production practice, in order to increase chip deformation, improve the strength of the tool tip and heat dissipation, a double-edged angle turning tool is used to achieve good chip breaking effect and widened the chip breaking range, as shown in Figure 1. The first edge inclination angle ls1 ≥ 0°, and the second edge inclination angle is close to the tool tip portion. Ls2 ≈ -20 °, the blade edge length of the second edge is lls2. ≈ap/3.
When the double-edged angle turning tool has g0=20°, a0=6°-8°, kr=90° or 75°, chamfering rake angle g01=-10°, re=0.15-0.2 mm. Cutting under conditions of Vc=80-100 m/min, f=0.2-0.3 mm/r, and ap=4-15 mm, the chip breaking effect is good and the tool durability is high.
It is required that the surface roughness value of the front and rear flank of the tool is small, and the tool blunting cone VB is 1/2 of the general processing material.
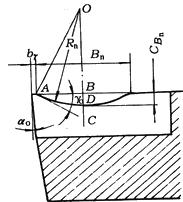
figure 2. Cutting stainless steel (roll) chipbreaker
The front angle of turning various stainless steels is approximately 12° to 30°. For martensitic stainless steel (such as 2Cr13), the rake angle can take a larger value; For austenitic and austenitic + ferritic stainless steels, the rake angle should be a small value; For stainless steels with low hardness after quenching and tempering or quenching and tempering, a larger rake angle may be adopted; For smaller diameter or thin-walled workpieces, a larger rake angle should be used.
High-speed steel milling cutter takes gn=10°~20°, and cemented carbide milling cutter takes gn=5°~10°; The reamer generally takes g0=8°~12°; the tap generally takes g0=15°~20° (machine) or g0=20° (hand).
Back angle a0: Increasing the relief angle reduces the friction between the flank and the machined surface, but reduces the strength and heat dissipation of the cutting edge. The reasonable value of the back angle depends on the cutting thickness, and the cutting thickness is small, and a larger relief angle should be selected.
Stainless steel turning tools or boring tools usually take a0=10°~20° (finishing) or a0=6°~10° (roughing); The high speed steel end mill takes a0=10°~20°, and the end mill takes a0=15°~20°; The hardness alloy end mill takes a0=5°~10°, and the end mill takes a0=12°~16°; The reamer and the tap take a0=8°~12°.

figure 1. Double edge angle chip breaking lathe tool
Reducing the tool's leading angle can increase the working length of the blade, which is good for heat dissipation. However, the radial force is increased during the cutting process, and vibration is easily generated, often taking kr=45°-75°. If the rigidity of the machine is insufficient, it can be increased appropriately. The secondary declination is usually taken as k'r = 8° to 15°. In order to strengthen the cutting edge, the cutting edge arc of e=0.5~1.0 mm should generally be ground.
Blade inclination ls:
In order to increase the strength of the tool tip, the inclination angle of the cutting edge is generally ls=-8° to -3°, and the larger value ls=-15° to -5° in the intermittent cutting.
In the production practice, in order to increase chip deformation, improve the strength of the tool tip and heat dissipation, a double-edged angle turning tool is used to achieve good chip breaking effect and widened the chip breaking range, as shown in Figure 1. The first edge inclination angle ls1 ≥ 0°, and the second edge inclination angle is close to the tool tip portion. Ls2 ≈ -20 °, the blade edge length of the second edge is lls2. ≈ap/3.
When the double-edged angle turning tool has g0=20°, a0=6°-8°, kr=90° or 75°, chamfering rake angle g01=-10°, re=0.15-0.2 mm. Cutting under conditions of Vc=80-100 m/min, f=0.2-0.3 mm/r, and ap=4-15 mm, the chip breaking effect is good and the tool durability is high.
It is required that the surface roughness value of the front and rear flank of the tool is small, and the tool blunting cone VB is 1/2 of the general processing material.

figure 2. Cutting stainless steel (roll) chipbreaker





