Gear Machining Method for Classifying
Selection of machining solutions for tooth blanks
For the tooth blanks of the shaft gear and the sleeve gear, the machining process is basically similar to that of the general shaft and the sleeve. Now, the processing of the disk gear blank is mainly discussed. The processing scheme of the tooth blank mainly depends on the wheel structure and production type of the gear.
1. The gear blank processing of mass production
When a large number of medium-sized tooth blanks are processed in large quantities, the process plan of “drilling one pull one multi-tool milling” is often adopted.
(1) Drilling or reaming with the outer circumference of the blank and the end face positioning.
(2) Pull holes.
Locating holes on Multi Tool semi-automatic lathes, rough and fine turning, end, grooving and chamfering.
This kind of process scheme can form an automatic assembly line due to the use of high-efficiency machine tools, so the production efficiency is high.
2. Batch production of blanks
When the gear blank batch production, often using "milling - pull - milling" process scheme
(1) Positioning the outer circle or wheel of the tooth blank, and finishing the outer circle, the end surface and the inner hole.
(2) Support the pull hole (or spline hole) with the end face.
(3) positioned in the hole and finishing cylindrical end surfaces.
This solution can be implemented by a horizontal lathe or a turret lathe and a broaching machine. It is characterized by stable processing quality and high production efficiency.
When the hole of the tooth has a step or a groove on the end face. It can make full use of the multi-tool on the turret lathe to carry out multi-station processing, and complete the processing of the tooth blank once on the turret lathe.
Gear tooth processing method
Gear and ring gear profile machining is the core of the whole gear processing.
The tooth profile of gears and ring gears is the core of the entire gear machining.
There are many processes in gear machining, which are for the machining of tooth profiles, with the aim of finally obtaining gears that meet the accuracy requirements.
According to the machining principle, the tooth profile can be divided into forming method and generating method.
Forming method: It is a method of cutting the tooth surface with a forming tool which is in conformity with the shape of the groove of the gear being cut, such as milling, drawing and forming grinding.
Generation method: The method of generating the tooth surface by the meshing relationship between the gear cutter and the workpiece according to the gear pair, such as hobbing, shaving, grinding and honing.
The choice of the tooth profile processing scheme depends mainly on the accuracy grade, structure shape, production type and production conditions of the gear.
For gears of different accuracy grades, the common tooth profile processing scheme is as follows:
(1) Gears below 8 degree accuracy
Hobbing or gear shaping can meet the requirements of tempered gears. Gear hobbing or gear shaping can meet the requirement of quenching and tempering gear.
For hardened gears may be employed: Rolling (insertion) teeth - tooth end machining - quenching - correction hole processing scheme. However, the accuracy of the tooth profile before quenching should be increased by one step.
(2) 6-7 precision gear
For hardened gears may be employed: Rough hobbing - fine hobbing - tooth end machining - fine shaving - surface hardening - calibration reference - caries.
(3) Gears with a precision of 5 or more
Generally adopted: Rough hobbing - fine hobbing - tooth end machining - quenching - calibration reference - coarse grinding - fine grinding teeth. Grinding is the processing method with the highest precision and the smallest surface roughness value in the current tooth profile processing. The highest precision can reach the level of 3-4.
1. Milling tooth
Gear accuracy grade: below 9
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 6.3~3.2μm
Scope of application: processing single-piece repairing, processing low-precision outer cylindrical gears, racks, bevel gears, worm gears
2. Pulling teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 1.6~0.4μm
Scope of application: mass production of 7-stage internal gears, external gear broaches are complex to manufacture, so use less
3. Hobbing
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 3.2~1.6μm
Scope of application: A variety of mass production, mass processing medium outer cylindrical gear and the worm wheel
4. Inserting teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 1.6μm
Scope of application: Medium-quality internal and external cylindrical gears, multiple gears and small racks in various mass production
5. Roller or Shaper - quenching - Honing gear
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.8~0.4μm
Scope of application: gears for tooth surface quenching
6. Rolling gear - Gear shaving
Gear accuracy grade: 7~6 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.8~0.4μm
Scope of application: mainly used for mass production
7. hobbing - Gear shaving - quenching - Honing gear
Gear accuracy grade: 7~6 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: mainly used for mass production
8. Rolling or shaping - quenching - grinding teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 6~3 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: For tooth surface machining of high-precision gears, low productivity and high cost
9. Rolling or shaping teeth - Gear grinding
Gear accuracy grade: 6~3 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: For tooth surface machining of high-precision gears, low productivity and high cost
8. Processing of the tooth end
The gear end of the gear is machined, rounded, inverted, chamfered and deburred.
The figure below is shown. When the gear is turned round and the tip is turned, it is easy to enter the meshing state when shifting gears, so as to reduce the impact phenomenon. Chamfering removes the tip of the tooth and the burr.
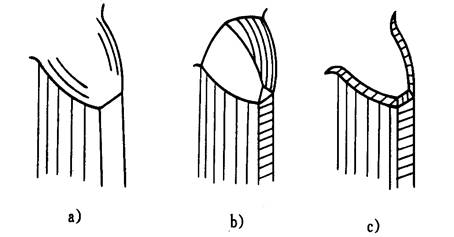
Tooth end machining
a) Reverse circle
b) Inverted tip
c) Chamfering
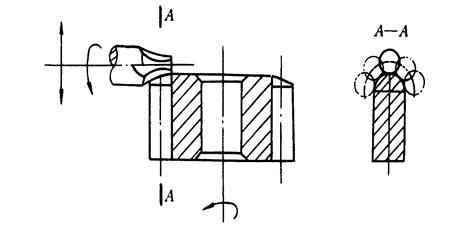
The figure below is a schematic diagram of the machining of the tooth end by rounding with a finger cutter. When rounding, the milling cutter rotates at high speed and swings along the arc. After machining one tooth, the workpiece retreats from the milling cutter, and after indexing, it quickly approaches the milling cutter to the tooth end of the next tooth. Tooth end machining must be performed before the gear is quenched, usually after rolling (inserting) the teeth, and the tooth end machining is arranged before shaving.
For the tooth blanks of the shaft gear and the sleeve gear, the machining process is basically similar to that of the general shaft and the sleeve. Now, the processing of the disk gear blank is mainly discussed. The processing scheme of the tooth blank mainly depends on the wheel structure and production type of the gear.
1. The gear blank processing of mass production
When a large number of medium-sized tooth blanks are processed in large quantities, the process plan of “drilling one pull one multi-tool milling” is often adopted.
(1) Drilling or reaming with the outer circumference of the blank and the end face positioning.
(2) Pull holes.
Locating holes on Multi Tool semi-automatic lathes, rough and fine turning, end, grooving and chamfering.
This kind of process scheme can form an automatic assembly line due to the use of high-efficiency machine tools, so the production efficiency is high.
2. Batch production of blanks
When the gear blank batch production, often using "milling - pull - milling" process scheme
(1) Positioning the outer circle or wheel of the tooth blank, and finishing the outer circle, the end surface and the inner hole.
(2) Support the pull hole (or spline hole) with the end face.
(3) positioned in the hole and finishing cylindrical end surfaces.
This solution can be implemented by a horizontal lathe or a turret lathe and a broaching machine. It is characterized by stable processing quality and high production efficiency.
When the hole of the tooth has a step or a groove on the end face. It can make full use of the multi-tool on the turret lathe to carry out multi-station processing, and complete the processing of the tooth blank once on the turret lathe.
Gear tooth processing method
Gear and ring gear profile machining is the core of the whole gear processing.
The tooth profile of gears and ring gears is the core of the entire gear machining.
There are many processes in gear machining, which are for the machining of tooth profiles, with the aim of finally obtaining gears that meet the accuracy requirements.
According to the machining principle, the tooth profile can be divided into forming method and generating method.
Forming method: It is a method of cutting the tooth surface with a forming tool which is in conformity with the shape of the groove of the gear being cut, such as milling, drawing and forming grinding.
Generation method: The method of generating the tooth surface by the meshing relationship between the gear cutter and the workpiece according to the gear pair, such as hobbing, shaving, grinding and honing.
The choice of the tooth profile processing scheme depends mainly on the accuracy grade, structure shape, production type and production conditions of the gear.
For gears of different accuracy grades, the common tooth profile processing scheme is as follows:
(1) Gears below 8 degree accuracy
Hobbing or gear shaping can meet the requirements of tempered gears. Gear hobbing or gear shaping can meet the requirement of quenching and tempering gear.
For hardened gears may be employed: Rolling (insertion) teeth - tooth end machining - quenching - correction hole processing scheme. However, the accuracy of the tooth profile before quenching should be increased by one step.
(2) 6-7 precision gear
For hardened gears may be employed: Rough hobbing - fine hobbing - tooth end machining - fine shaving - surface hardening - calibration reference - caries.
(3) Gears with a precision of 5 or more
Generally adopted: Rough hobbing - fine hobbing - tooth end machining - quenching - calibration reference - coarse grinding - fine grinding teeth. Grinding is the processing method with the highest precision and the smallest surface roughness value in the current tooth profile processing. The highest precision can reach the level of 3-4.
1. Milling tooth
Gear accuracy grade: below 9
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 6.3~3.2μm
Scope of application: processing single-piece repairing, processing low-precision outer cylindrical gears, racks, bevel gears, worm gears
2. Pulling teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 1.6~0.4μm
Scope of application: mass production of 7-stage internal gears, external gear broaches are complex to manufacture, so use less
3. Hobbing
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 3.2~1.6μm
Scope of application: A variety of mass production, mass processing medium outer cylindrical gear and the worm wheel
4. Inserting teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 1.6μm
Scope of application: Medium-quality internal and external cylindrical gears, multiple gears and small racks in various mass production
5. Roller or Shaper - quenching - Honing gear
Gear accuracy grade: 8~7 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.8~0.4μm
Scope of application: gears for tooth surface quenching
6. Rolling gear - Gear shaving
Gear accuracy grade: 7~6 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.8~0.4μm
Scope of application: mainly used for mass production
7. hobbing - Gear shaving - quenching - Honing gear
Gear accuracy grade: 7~6 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: mainly used for mass production
8. Rolling or shaping - quenching - grinding teeth
Gear accuracy grade: 6~3 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: For tooth surface machining of high-precision gears, low productivity and high cost
9. Rolling or shaping teeth - Gear grinding
Gear accuracy grade: 6~3 level
Tooth surface roughness Ra: 0.4~0.2μm
Scope of application: For tooth surface machining of high-precision gears, low productivity and high cost
8. Processing of the tooth end
The gear end of the gear is machined, rounded, inverted, chamfered and deburred.
The figure below is shown. When the gear is turned round and the tip is turned, it is easy to enter the meshing state when shifting gears, so as to reduce the impact phenomenon. Chamfering removes the tip of the tooth and the burr.

Tooth end machining
a) Reverse circle
b) Inverted tip
c) Chamfering
The figure below is a schematic diagram of the machining of the tooth end by rounding with a finger cutter. When rounding, the milling cutter rotates at high speed and swings along the arc. After machining one tooth, the workpiece retreats from the milling cutter, and after indexing, it quickly approaches the milling cutter to the tooth end of the next tooth. Tooth end machining must be performed before the gear is quenched, usually after rolling (inserting) the teeth, and the tooth end machining is arranged before shaving.






