Process for turning precision rollers
The roller is the main part on the rolling mill. In the actual use process, due to a certain impact force, and the surface will be rubbed by high-speed, high-temperature red steel. The surface is required to have good wear resistance, and at the same time, it must have sufficient toughness to prevent breakage by impact.
In view of the special use of the roller, it is determined that its material must have:
1. High speed wear resistance;
2, enough red hardness;
3. Sufficient strength and toughness.
In the actual use process, approx. white cast iron is more suitable. However, since this material is generally used in an as-cast state, casting defects are inevitably present and the hardness can reach 50 to 60 HRC. In addition, the roller (as shown in the drawing) has higher coaxiality requirements, which brings great difficulties to turning.
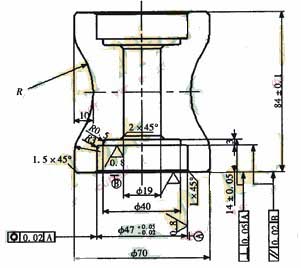
Figure. Roller
In view of the special use of the roller, it is determined that its material must have:
1. High speed wear resistance;
2, enough red hardness;
3. Sufficient strength and toughness.
In the actual use process, approx. white cast iron is more suitable. However, since this material is generally used in an as-cast state, casting defects are inevitably present and the hardness can reach 50 to 60 HRC. In addition, the roller (as shown in the drawing) has higher coaxiality requirements, which brings great difficulties to turning.

Figure. Roller
I. Reasonable choice of tool grade
The strength and hardness of the roller material have reached the strength and hardness of the ordinary cemented carbide tool (YT), so the ordinary tool can not cut normally. Although the hardness can be appropriately reduced by quenching and tempering, and the cutting process is facilitated, the cost is too large and the cycle is long, so the as-cast direct processing is selected.
Trial processing and repeated comparisons of various high hardness tools, including ceramic tools and imported tools.
Finally, the YS8 grade turning tool with hardness and wear resistance that meets the cutting requirements and relatively low price is selected for turning.
Of course, for the use of rollers which required repair, since during use corresponds to a time to work hardening and quenching, particularly high hardness. In the case where it is not possible to cut with a YS8 tool, we use a ceramic blade for repair processing.
II. Reasonable choice of tool geometry and cutting amount
Because there are considerable elements such as Cr and Mo in the blank, the plasticity is good, the strength and hardness are high, the deformation resistance is large, and the cutting force is 2 to 3 times higher than that of ordinary steel. The cutting heat also increases, the thermal conductivity is low, the heat dissipation is difficult, the cutting zone temperature is extremely high, and the tool is easily damaged.
In addition, the blank is a casting, and there are defects such as surface hard skin, pores, sand holes, uneven machining allowance, and uneven hardness of the material, which inevitably leads to an increase in processing instability. Reduced tool life, increased production costs and reduced production efficiency. In response to these factors, we have to improve the cutting process by a reasonable choice of cutting parameters.
1, roughing
When roughing, the surface of the machined surface is not uniform, and the surface of the blank has a hard skin. Therefore, the maximum depth of cut should be chosen, and the greater the depth of cut, the higher the cutting heat generated and the greater the cutting force the tool can withstand. In order to allow the tool to withstand sufficient compressive stress, the negative rake angle and negative rake angle (0° ~ -5°) are used to increase the rigidity of the tool; The back angle is generally between 6° and 8°, the lead angle is between 10° and 30°, and the secondary declination is between 10° and 15°. Due to the high hardness of the blank and poor heat dissipation, a low speed (80r/min) is used in roughing; Small feed rate (0.15mm/r) to properly reduce cutting force; The cutting depth is selected between 2 and 3 mm.
2, finishing
Because the depth of cut is small, the cutting force is small and the cutting heat is small. In order to improve the surface quality, a large rake angle is adopted, and the back angle takes a large value of 10°. Minimize the friction and extrusion of the tool and the workpiece to improve the surface quality of the workpiece. The lead angle is between 10° and 30°; the secondary declination is between 5° and 10°. In order to avoid the chip flowing out and scratching the processed surface, the positive blade inclination angle is taken between 0° and 5°; Use a higher spindle speed (120r/min); Small depth of cut (0.2 to 0.3 mm) and small feed rate of 0.1 mm/r.
3, Arc surface processing
When turning the outer circle, inner hole and total length, it is more economical to process on an ordinary lathe. However, the circular surface is not easy to guarantee on the ordinary lathe, so the arc surface of the roller is completed by a CNC lathe. For the uneven margin, the material is hard. When programming, increase the number of passes and set the low spindle speed and small feed. For the case where the sand hole and the air hole are easy to cause the blade to chip, the program starting point is set every time before the tool is programmed. Avoiding the “starting from scratch” process after each knife breaks can save a lot of time and reduce “useless work” to increase production efficiency.
The strength and hardness of the roller material have reached the strength and hardness of the ordinary cemented carbide tool (YT), so the ordinary tool can not cut normally. Although the hardness can be appropriately reduced by quenching and tempering, and the cutting process is facilitated, the cost is too large and the cycle is long, so the as-cast direct processing is selected.
Trial processing and repeated comparisons of various high hardness tools, including ceramic tools and imported tools.
Finally, the YS8 grade turning tool with hardness and wear resistance that meets the cutting requirements and relatively low price is selected for turning.
Of course, for the use of rollers which required repair, since during use corresponds to a time to work hardening and quenching, particularly high hardness. In the case where it is not possible to cut with a YS8 tool, we use a ceramic blade for repair processing.
II. Reasonable choice of tool geometry and cutting amount
Because there are considerable elements such as Cr and Mo in the blank, the plasticity is good, the strength and hardness are high, the deformation resistance is large, and the cutting force is 2 to 3 times higher than that of ordinary steel. The cutting heat also increases, the thermal conductivity is low, the heat dissipation is difficult, the cutting zone temperature is extremely high, and the tool is easily damaged.
In addition, the blank is a casting, and there are defects such as surface hard skin, pores, sand holes, uneven machining allowance, and uneven hardness of the material, which inevitably leads to an increase in processing instability. Reduced tool life, increased production costs and reduced production efficiency. In response to these factors, we have to improve the cutting process by a reasonable choice of cutting parameters.
1, roughing
When roughing, the surface of the machined surface is not uniform, and the surface of the blank has a hard skin. Therefore, the maximum depth of cut should be chosen, and the greater the depth of cut, the higher the cutting heat generated and the greater the cutting force the tool can withstand. In order to allow the tool to withstand sufficient compressive stress, the negative rake angle and negative rake angle (0° ~ -5°) are used to increase the rigidity of the tool; The back angle is generally between 6° and 8°, the lead angle is between 10° and 30°, and the secondary declination is between 10° and 15°. Due to the high hardness of the blank and poor heat dissipation, a low speed (80r/min) is used in roughing; Small feed rate (0.15mm/r) to properly reduce cutting force; The cutting depth is selected between 2 and 3 mm.
2, finishing
Because the depth of cut is small, the cutting force is small and the cutting heat is small. In order to improve the surface quality, a large rake angle is adopted, and the back angle takes a large value of 10°. Minimize the friction and extrusion of the tool and the workpiece to improve the surface quality of the workpiece. The lead angle is between 10° and 30°; the secondary declination is between 5° and 10°. In order to avoid the chip flowing out and scratching the processed surface, the positive blade inclination angle is taken between 0° and 5°; Use a higher spindle speed (120r/min); Small depth of cut (0.2 to 0.3 mm) and small feed rate of 0.1 mm/r.
3, Arc surface processing
When turning the outer circle, inner hole and total length, it is more economical to process on an ordinary lathe. However, the circular surface is not easy to guarantee on the ordinary lathe, so the arc surface of the roller is completed by a CNC lathe. For the uneven margin, the material is hard. When programming, increase the number of passes and set the low spindle speed and small feed. For the case where the sand hole and the air hole are easy to cause the blade to chip, the program starting point is set every time before the tool is programmed. Avoiding the “starting from scratch” process after each knife breaks can save a lot of time and reduce “useless work” to increase production efficiency.





