3D Printing Technology Explained
3D printing technology has begun to be widely used in various fields in foreign countries to help people improve development efficiency and reduce production costs, 3D printers have begun to spread.
In China, due to the late start, it is still widely used. The main reasons are:
1. There is still a long way to go before the market is nurtured. At present, most manufacturing companies in China have not yet accepted such advanced manufacturing concepts as “digital design” and “low-volume batch production”. The lack of understanding of the strategic significance of this emerging technology, 3D printing, does not understand what this emerging technology can do and how much value it can create.
2. Enterprise-level, professional-grade 3D printing devices and their materials are also relatively expensive and their acceptance by customers is low. Although there are already some 3D printers on the market with prices as low as a few thousand, this entry-level 3D printer is more suitable for purchase by individuals and enthusiasts. It is difficult to use in industrial manufacturing, construction engineering and other fields, not to mention professional applications such as aerospace and medical. The price of professional-grade 3D printing equipment is often in the range of hundreds of thousands and even millions, making many companies concerned about 3D printing technology prohibitive.
3. The variety of materials is not enough and it also limits the promotion of 3D printing technology. Although in terms of plastic materials, there are already hundreds of them, from elastic to rigid, from heat-melting to high-temperature resistant, from transparent to opaque, from biocompatible to castable. There are many kinds of materials, but they are still inferior to those of traditional materials.
4. The three-dimensional digitization technology has not yet been popularized, which also limits the market space for 3D printers. Because the premise of 3D printing is that the computer has a three-dimensional data to be printed, the acquisition and creation of three-dimensional data is still a technical activity for the general public. The strongest domestic digital professional field is Hangzhou Xianlin 3D Technology Co., Ltd., which independently developed a variety of three-dimensional scanners for different application areas. Can help to quickly obtain 3D data of the object, the output STL digital model can be used for 3D printing, Less than CAD modeling technology requirements, faster.
Currently, there are more than a dozen different 3D printer molding technologies on the market. Including SLS, DMLS, FDM, SLA, DLP, FFF, MEM, LOM, EBM, SHS, 3DP, etc., 3D printers of different technology types need different materials to print finished products. Among them, SLS, FDM, SLA, LOM, and 3DP are more mature.
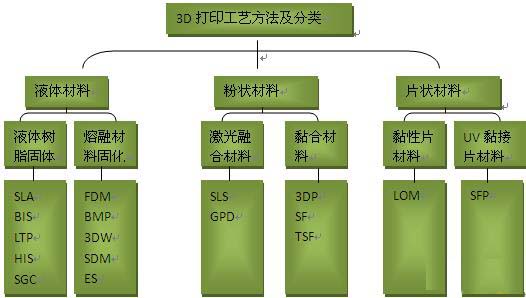
Liquid material
Liquid Resin Solids: SLA, BIS, LTP, HIS, SGC
Molten Material Curing: FDM, BMP, 3DW, SDM, ES
Powdery material
Laser fusion materials SLS, GPD
Adhesive material 3DP, SF, TSF
Sheet material
Adhesive sheet material LOM
UV adhesive sheet material SFP
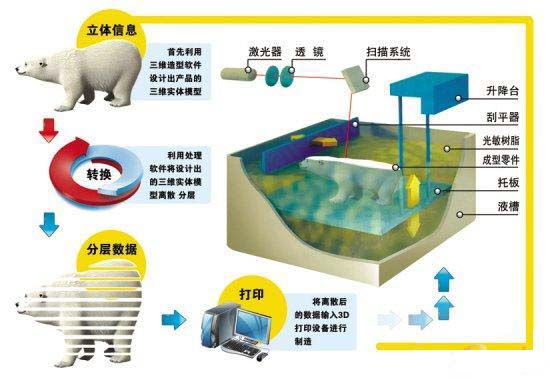
1.1 SLA (Stereo lithography Appearance)
Lasers with specific wavelengths and intensities are focused on the surface of the light-curing material (liquid photosensitive resin material) so that they are spot-to-line and solidified in a line-to-face sequence to complete a drawing operation for one layer. The elevator table then moves the height of one ply in the vertical direction and solidifies the other. This layer stacks up to form a three-dimensional entity.
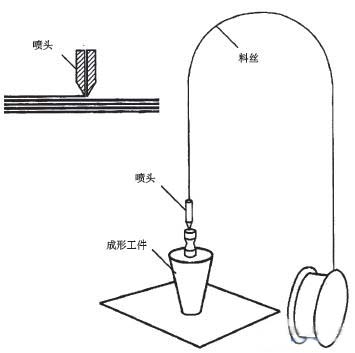
3.2 FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
The method uses a filamentous material (paraffin, metal, plastic, low-melting-point alloy wire) as a raw material. The electric heating method is used to heat the silk material to slightly higher than the melting temperature (about 1°C higher than the melting point), Under the control of the computer, the showerhead moves in a plane and the molten material is coated on the workbench. After cooling, a layer of cross-section of the workpiece is formed. After one layer is formed, the nozzle is moved to a layer of height, and the next layer of coating is applied, so that the three-dimensional workpiece is formed layer by layer.
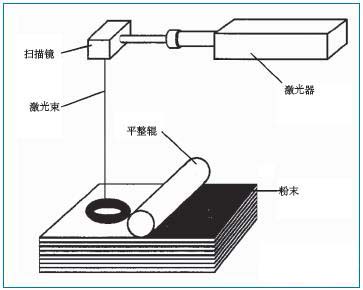
1.3 SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
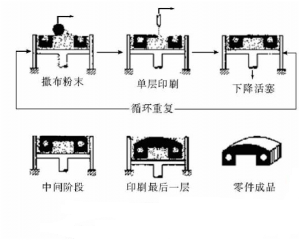
The entire process device consists of a powder cylinder and a forming cylinder. When working, the powder cylinder piston (powder feed piston) rises and the powder is evenly spread on the piston (working piston) of the forming cylinder by the powder spreading roller. The computer controls the two-dimensional scanning trajectory of the laser beam according to the prototype's slice model and selectively sinters the solid powder material to form a layer of the part. After the powder has completed a layer, the working piston drops one layer thick and the powder spreading system is covered with new powder. Control the laser beam and scan the new layer again. This cycle, stacking layers until the three-dimensional parts shape. Finally, the unsintered powder is recovered in the powder tank and the molded part is taken out. For metal powder laser sintering, the entire table is heated to a certain temperature before sintering, which reduces hot deformation during molding and facilitates the bond between the layers.
 1.4 3DP (Three-Dimensional Printing)
1.4 3DP (Three-Dimensional Printing)
The 3DP process is similar to the SLS process and is formed using powder materials such as ceramic powders, metal powders. The difference is that the powder of the material is not connected by sintering, but the cross-section of the part is "printed" on top of the material powder by an adhesive (such as silica gel) by the spray head. Parts bonded with adhesives have low strength and must be post-treated. The specific process is as follows: After the upper layer is bonded, the forming cylinder is lowered by a distance (equal to the layer thickness: 0.013 to 0.1 mm), the powder cylinder is raised by a height, a number of powders are pushed out, and the powder spreading roller is pushed to the forming cylinder. Paved and compacted. The showerhead is under the control of a computer and presses a forming section of the forming data to selectively inject the adhesive build layer. Excess powder is collected by the powder collecting device when spreading the powder roller. In this way powder is fed and sprayed on the binder to finally complete the bonding of a three-dimensional powder. The place where the adhesive is not sprayed is dry powder, which plays a supporting role in the forming process, and it is relatively easy to remove after forming.
 1.5 LOM (Laminated Object Manufacturing)
1.5 LOM (Laminated Object Manufacturing)
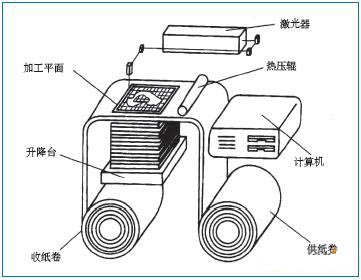
LOM is a layered solid manufacturing method, also known as stacking method, It uses sheets (such as paper sheets, plastic films, or composite materials) as the raw material. The laser cutting system uses computer-extracted cross-sectional outline data to cut the inside and outside contours of the workpieces with lasers using paper coated with hot melt adhesive on the back. After one layer is cut, the feeding mechanism superimposes a new layer of paper, bonds the cut layers together using a hot-pressure adhesive device, and then cuts them so that the layers are cut, bonded, and finally become three-dimensional workpieces. .
In China, due to the late start, it is still widely used. The main reasons are:
1. There is still a long way to go before the market is nurtured. At present, most manufacturing companies in China have not yet accepted such advanced manufacturing concepts as “digital design” and “low-volume batch production”. The lack of understanding of the strategic significance of this emerging technology, 3D printing, does not understand what this emerging technology can do and how much value it can create.
2. Enterprise-level, professional-grade 3D printing devices and their materials are also relatively expensive and their acceptance by customers is low. Although there are already some 3D printers on the market with prices as low as a few thousand, this entry-level 3D printer is more suitable for purchase by individuals and enthusiasts. It is difficult to use in industrial manufacturing, construction engineering and other fields, not to mention professional applications such as aerospace and medical. The price of professional-grade 3D printing equipment is often in the range of hundreds of thousands and even millions, making many companies concerned about 3D printing technology prohibitive.
3. The variety of materials is not enough and it also limits the promotion of 3D printing technology. Although in terms of plastic materials, there are already hundreds of them, from elastic to rigid, from heat-melting to high-temperature resistant, from transparent to opaque, from biocompatible to castable. There are many kinds of materials, but they are still inferior to those of traditional materials.
4. The three-dimensional digitization technology has not yet been popularized, which also limits the market space for 3D printers. Because the premise of 3D printing is that the computer has a three-dimensional data to be printed, the acquisition and creation of three-dimensional data is still a technical activity for the general public. The strongest domestic digital professional field is Hangzhou Xianlin 3D Technology Co., Ltd., which independently developed a variety of three-dimensional scanners for different application areas. Can help to quickly obtain 3D data of the object, the output STL digital model can be used for 3D printing, Less than CAD modeling technology requirements, faster.
Currently, there are more than a dozen different 3D printer molding technologies on the market. Including SLS, DMLS, FDM, SLA, DLP, FFF, MEM, LOM, EBM, SHS, 3DP, etc., 3D printers of different technology types need different materials to print finished products. Among them, SLS, FDM, SLA, LOM, and 3DP are more mature.

Liquid material
Liquid Resin Solids: SLA, BIS, LTP, HIS, SGC
Molten Material Curing: FDM, BMP, 3DW, SDM, ES
Powdery material
Laser fusion materials SLS, GPD
Adhesive material 3DP, SF, TSF
Sheet material
Adhesive sheet material LOM
UV adhesive sheet material SFP
1.1 SLA (Stereo lithography Appearance)
Lasers with specific wavelengths and intensities are focused on the surface of the light-curing material (liquid photosensitive resin material) so that they are spot-to-line and solidified in a line-to-face sequence to complete a drawing operation for one layer. The elevator table then moves the height of one ply in the vertical direction and solidifies the other. This layer stacks up to form a three-dimensional entity.

3.2 FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
The method uses a filamentous material (paraffin, metal, plastic, low-melting-point alloy wire) as a raw material. The electric heating method is used to heat the silk material to slightly higher than the melting temperature (about 1°C higher than the melting point), Under the control of the computer, the showerhead moves in a plane and the molten material is coated on the workbench. After cooling, a layer of cross-section of the workpiece is formed. After one layer is formed, the nozzle is moved to a layer of height, and the next layer of coating is applied, so that the three-dimensional workpiece is formed layer by layer.

1.3 SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
The entire process device consists of a powder cylinder and a forming cylinder. When working, the powder cylinder piston (powder feed piston) rises and the powder is evenly spread on the piston (working piston) of the forming cylinder by the powder spreading roller. The computer controls the two-dimensional scanning trajectory of the laser beam according to the prototype's slice model and selectively sinters the solid powder material to form a layer of the part. After the powder has completed a layer, the working piston drops one layer thick and the powder spreading system is covered with new powder. Control the laser beam and scan the new layer again. This cycle, stacking layers until the three-dimensional parts shape. Finally, the unsintered powder is recovered in the powder tank and the molded part is taken out. For metal powder laser sintering, the entire table is heated to a certain temperature before sintering, which reduces hot deformation during molding and facilitates the bond between the layers.

The 3DP process is similar to the SLS process and is formed using powder materials such as ceramic powders, metal powders. The difference is that the powder of the material is not connected by sintering, but the cross-section of the part is "printed" on top of the material powder by an adhesive (such as silica gel) by the spray head. Parts bonded with adhesives have low strength and must be post-treated. The specific process is as follows: After the upper layer is bonded, the forming cylinder is lowered by a distance (equal to the layer thickness: 0.013 to 0.1 mm), the powder cylinder is raised by a height, a number of powders are pushed out, and the powder spreading roller is pushed to the forming cylinder. Paved and compacted. The showerhead is under the control of a computer and presses a forming section of the forming data to selectively inject the adhesive build layer. Excess powder is collected by the powder collecting device when spreading the powder roller. In this way powder is fed and sprayed on the binder to finally complete the bonding of a three-dimensional powder. The place where the adhesive is not sprayed is dry powder, which plays a supporting role in the forming process, and it is relatively easy to remove after forming.

LOM is a layered solid manufacturing method, also known as stacking method, It uses sheets (such as paper sheets, plastic films, or composite materials) as the raw material. The laser cutting system uses computer-extracted cross-sectional outline data to cut the inside and outside contours of the workpieces with lasers using paper coated with hot melt adhesive on the back. After one layer is cut, the feeding mechanism superimposes a new layer of paper, bonds the cut layers together using a hot-pressure adhesive device, and then cuts them so that the layers are cut, bonded, and finally become three-dimensional workpieces. .






