Anodizing
What is anodizing?
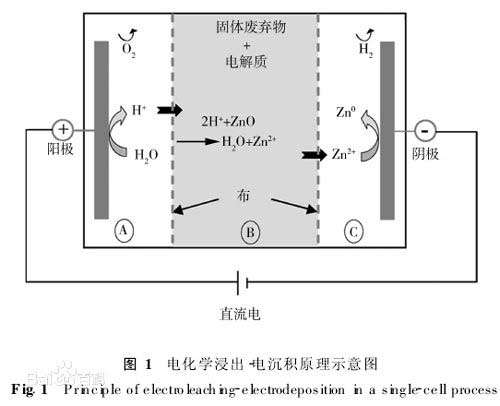
Anodic oxidation: The electrochemical oxidation of a metal or alloy. A process in which aluminum and its alloys form an oxide film on an aluminum product (anode) due to an applied current under a corresponding electrolyte and a specific process condition. Anodization is usually anodization of sulfuric acid unless otherwise specified.
In order to overcome the defects in surface hardness and wear resistance of aluminum alloys, the scope of application is extended and the service life is extended. Surface treatment technology has become an indispensable part in the use of aluminum alloys, and anodizing technology is currently the most widely used and most successful.
Principle
The so-called anodization of aluminum is an electrolytic oxidation process in which the surfaces of aluminum and aluminum alloys are generally converted into an oxide film, which has protective, decorative and some other functional properties. The anodization of aluminum starting from this definition includes only the part of the process of forming an anodized film.
The metal or alloy part is used as an anode, and an oxide film is formed on the surface by electrolysis. The metal oxide film changes the surface state and properties such as surface coloration, improves corrosion resistance, enhances wear resistance and hardness, and protects metal surfaces. For example, anodization of aluminum. Aluminum and its alloy are placed in the corresponding electrolyte (such as sulfuric acid, chromic acid, oxalic acid, etc.) as the anode, under specific conditions and under the action of the applied current, electrolysis. Anodized aluminum or its alloy is oxidized, a thin layer of aluminum oxide is formed on the surface, its thickness is 5-30 micrometers, and the hard anodized film can reach 25-150 micrometers. After anodized aluminum or its alloys, improve its hardness and wear resistance, up to 250 ~ 500 kg/mm2, good heat resistance, hard anodized film melting point up to 2320K, excellent insulation, resistance to fire With a voltage of up to 2000V, corrosion resistance is enhanced, and corrosion does not occur for thousands of hours in ω=0.03NaCl salt spray. Oxide film has a large number of micro-holes in the thin layer, can absorb a variety of lubricants, suitable for the manufacture of engine cylinders or other wear parts; The strong adsorption capacity of membrane pores can be colored into various bright colors. Non-ferrous metals or their alloys (such as aluminum, magnesium, and their alloys) can be anodized. This method is widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft parts, precision instruments and radio equipment, daily necessities and architectural decoration.
In general, anodes use aluminum or aluminum alloys as anodes, while cathodes use lead plates. The aluminum and lead plates are placed together in an aqueous solution where sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, etc. are used for electrolysis to form an oxide film on the surfaces of the aluminum and lead plates. Among these acids, the most widely used is anodization with sulfuric acid.


Other types
In addition to metals, the oxidation caused by other substances as anodes is also referred to as "anodization."
In the actual process, the anodization of aluminum alloys is relatively large and can be applied in daily life. Considering the characteristics of this process, a hard protective layer is produced on the surface of the aluminum part, which can be used for the production of daily necessities such as kitchen utensils.
However, the anodizing effect of cast aluminum is not good, the surface is not bright, and it can only be black. Aluminum profiles will be better.
Effect
Protective
Decorative
Insulation
Improves adhesion to organic coatings
Improve the bonding with inorganic coatings
Other features in development
Difference
The difference between anodized and conductive oxidation
1) Anodizing is performed under high voltage conditions, which is an electrochemical reaction process; The conductive oxide (also known as chemical oxidation) does not require power, only need to soak in the syrup on the line where it is a pure chemical reaction.
2) Anodizing requires a long time, often tens of minutes, while conductive oxidation requires only a few tens of seconds.
3) The anodized film has several micrometers to several tens of micrometers, and it is hard and wear-resistant; The film formed by the conductive oxidation is only 0.01-0.15 micrometers, the wear resistance is not very good, but it is both conductive and resistant to atmospheric corrosion, which is its advantage.
4) The oxide film is inherently non-conductive, but since the film formed by the conductive oxidation is very thin, it is electrically conductive.


Anodic oxidation: The electrochemical oxidation of a metal or alloy. A process in which aluminum and its alloys form an oxide film on an aluminum product (anode) due to an applied current under a corresponding electrolyte and a specific process condition. Anodization is usually anodization of sulfuric acid unless otherwise specified.
In order to overcome the defects in surface hardness and wear resistance of aluminum alloys, the scope of application is extended and the service life is extended. Surface treatment technology has become an indispensable part in the use of aluminum alloys, and anodizing technology is currently the most widely used and most successful.
Principle
The so-called anodization of aluminum is an electrolytic oxidation process in which the surfaces of aluminum and aluminum alloys are generally converted into an oxide film, which has protective, decorative and some other functional properties. The anodization of aluminum starting from this definition includes only the part of the process of forming an anodized film.
The metal or alloy part is used as an anode, and an oxide film is formed on the surface by electrolysis. The metal oxide film changes the surface state and properties such as surface coloration, improves corrosion resistance, enhances wear resistance and hardness, and protects metal surfaces. For example, anodization of aluminum. Aluminum and its alloy are placed in the corresponding electrolyte (such as sulfuric acid, chromic acid, oxalic acid, etc.) as the anode, under specific conditions and under the action of the applied current, electrolysis. Anodized aluminum or its alloy is oxidized, a thin layer of aluminum oxide is formed on the surface, its thickness is 5-30 micrometers, and the hard anodized film can reach 25-150 micrometers. After anodized aluminum or its alloys, improve its hardness and wear resistance, up to 250 ~ 500 kg/mm2, good heat resistance, hard anodized film melting point up to 2320K, excellent insulation, resistance to fire With a voltage of up to 2000V, corrosion resistance is enhanced, and corrosion does not occur for thousands of hours in ω=0.03NaCl salt spray. Oxide film has a large number of micro-holes in the thin layer, can absorb a variety of lubricants, suitable for the manufacture of engine cylinders or other wear parts; The strong adsorption capacity of membrane pores can be colored into various bright colors. Non-ferrous metals or their alloys (such as aluminum, magnesium, and their alloys) can be anodized. This method is widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft parts, precision instruments and radio equipment, daily necessities and architectural decoration.
In general, anodes use aluminum or aluminum alloys as anodes, while cathodes use lead plates. The aluminum and lead plates are placed together in an aqueous solution where sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, chromic acid, etc. are used for electrolysis to form an oxide film on the surfaces of the aluminum and lead plates. Among these acids, the most widely used is anodization with sulfuric acid.


Other types
In addition to metals, the oxidation caused by other substances as anodes is also referred to as "anodization."
In the actual process, the anodization of aluminum alloys is relatively large and can be applied in daily life. Considering the characteristics of this process, a hard protective layer is produced on the surface of the aluminum part, which can be used for the production of daily necessities such as kitchen utensils.
However, the anodizing effect of cast aluminum is not good, the surface is not bright, and it can only be black. Aluminum profiles will be better.
Effect
Protective
Decorative
Insulation
Improves adhesion to organic coatings
Improve the bonding with inorganic coatings
Other features in development
Difference
The difference between anodized and conductive oxidation
1) Anodizing is performed under high voltage conditions, which is an electrochemical reaction process; The conductive oxide (also known as chemical oxidation) does not require power, only need to soak in the syrup on the line where it is a pure chemical reaction.
2) Anodizing requires a long time, often tens of minutes, while conductive oxidation requires only a few tens of seconds.
3) The anodized film has several micrometers to several tens of micrometers, and it is hard and wear-resistant; The film formed by the conductive oxidation is only 0.01-0.15 micrometers, the wear resistance is not very good, but it is both conductive and resistant to atmospheric corrosion, which is its advantage.
4) The oxide film is inherently non-conductive, but since the film formed by the conductive oxidation is very thin, it is electrically conductive.






