Sheet metal is a comprehensive cold-working process for metal materials (usually under 6mm plate). Including cutting, punching/cutting/composite, folding, riveting, splicing, forming (such as car body) and so on. Its distinguishing feature is the uniform thickness of the part.
Sheet metal processing, sheet metal processing manufacturers, stainless steel sheet metal processing, chassis sheet metal processing, sheet metal manufacturers, precision sheet metal processing, sheet metal processing, sheet metal bending processing, Sheet metal molding
Sheet metal processing includes conventional methods such as cutting blanking, blanking, bending and forming, and various process parameters. It also includes various cold stamping die structure and process parameters, various equipment working principles and operating methods, and also includes new stamping techniques. And new technology.
Technology
Through NCT (CNC punching), laser (laser cutting machine), CNC bending machine tools, rivets and other processing tools for processing sheet metal, generally used for sample production, the cost is higher.
2. Mold processing:
Through the fixed mold, processing sheet metal. Generally, there are blanking molds and forming molds, which are mainly used for mass production and have lower costs.
3. NCT (CNC machine) processing
Common uses of CNC machine tools: blanking, punching net holes, punching convex hulls, trimming edges, bumps, pressure ribs, pressure lines, pumping holes. (Pressing line, is a variety of post-embossing processing methods, such as bronzing, convex, embossed, plastic, pressure line, beer, stick, cut, etc. are all postpress processing.
The minimum distance between two pressure lines is generally 3mm, but it also varies slightly depending on the processing object. ) CNC machining accuracy: +/- 0.1mm.
4. Laser (laser cutting) processing
Laser cutting is the use of electron discharge as the energy source, through He, N2, CO2 and other mixed gases as the excitation medium, the use of a group of mirrors to produce a focused laser beam, so as to cut the material.
Driven by a programmable servo motor, the cutting head moves according to a predetermined path to cut various shapes of workpieces. Common Uses of Laser Machines: Cutting, Shape Cutting, Secondary Cutting, Cutting Lines, Machining Accuracy of Cutting Shaped Hole Laser Machine: +/-0.1mm
5. Folding bed processing
Bending processing fixes the upper and lower molds on the upper and lower worktables of the folding bed, and uses hydraulic transmission to drive the relative movement of the worktable. In combination with the shape of the lower die, bending of the sheet is achieved.
It is generally divided into up and down movements. The basic principle of the bending process sequence: bending from inside to outside. Bending from small to large. First fold the special shape, then fold the general shape.
After the former process is formed, there is no interference with the subsequent process.
Bend processing accuracy:
One fold: +/-0.1mm
Two fold: +/-0.2mm
Tri-fold: +/-0.3mm
6. Clamp processing
Crossed, Chisel cut, Sawing, Tumble, drilling, Reaming, Countersink holes,Tapping threads and sets of threads, straightening and bending, riveting, scraping, grinding, technical measurement, simple heat treatment, etc., and can be assembled, commissioning and maintenance of the machine or parts.
1) Processed parts:
Some machining methods that are not suitable or cannot be solved by mechanical methods can be completed by fitters. Such as: the part of the process of marking, precision processing (for example, scraping and cutting template and making molds, etc.) and inspection and repair and so on.
2) Assembly:
Parts are assembled according to assembly technology requirements for mechanical equipment, component assembly and final assembly. And make adjustments, inspections and commissioning, etc. to become qualified machinery equipment
3) Equipment maintenance: When the machinery is in use, there is a fault, damage occurs or the precision is reduced after long-term use. When affecting the use, it is also necessary to carry out maintenance and repairs through fitters.
4) Manufacturing and repair of tools: Manufacturing and repairing various tools, fixtures, measuring tools, molds and various specialized equipment.
7. Sheet metal connection
The connection methods between sheet metal parts mainly include: locking screws, rivet pull rivets, pumping holes riveting, hook card slot, spot welding and hinged connections.
(1) Lock screw: The lock screw is the most commonly used connection method at present
① Principle: In the connected two parts, there is a part of the tooth hole, only punch on the other part; Tapping on tooth extraction (Tapping in two ways: Self-tapping - Tapping a screw while tapping a screw with a tapping screw; A tapping machine tapping.) Finally connected with screws.
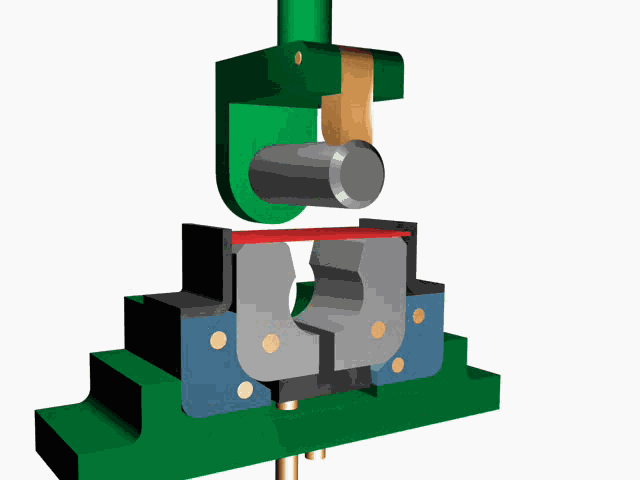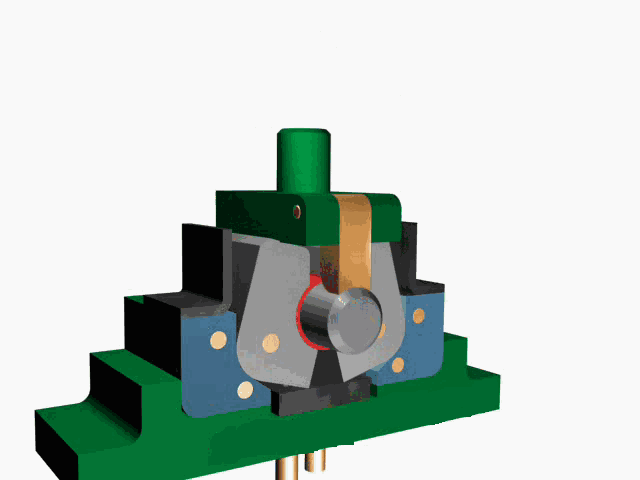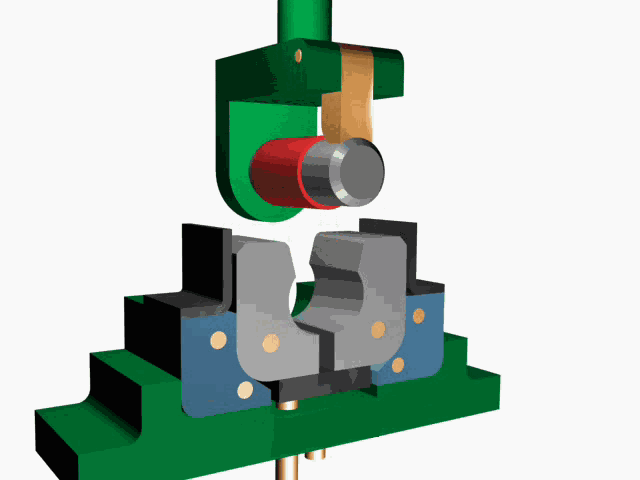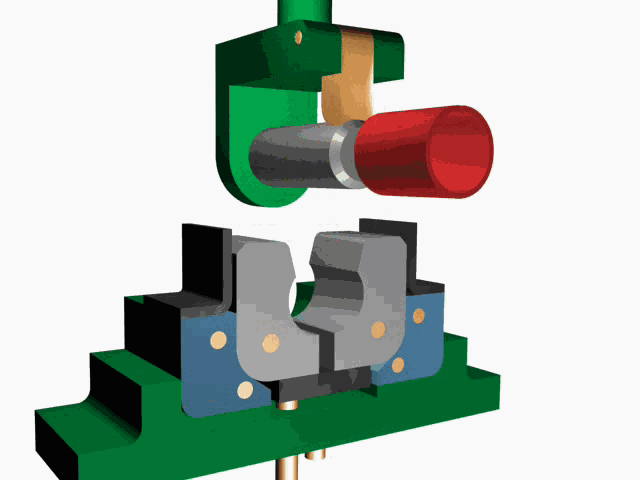
(2) Pull rivets:
① Principle: As shown in FIG 3, the two parts of the pull stud is inserted into a corresponding hole, Pull the pull rod 4 with a pull gun until it breaks. The pull rod head 1 moves downwards, so that the outer pull sleeve 3 that is outsourced becomes larger and larger than the diameter of the hole. In order to achieve the purpose of connecting two parts.
(3) Suction hole riveting:
① Principle: As shown in Figure 5, Part 1 (with C'sink hole) and Part 2 (with Extrude hole), Extrude hole is opened by a mold and filled in the corner hole of the C'sink hole to connect the two parts together.
(4) Spot welding:
① Advantages: Spot welding fastening, for suppliers to complete, easy production line operation, low cost (about 0.05HKD for spot welding); parts without complicated structure, simple mold
(5)Clasp card position
① Features: Clasp card position connection is generally prepositioned, can not directly fasten the parts, usually with the lock screw and rivet pull riveting and other connections with the use.
(6) Hinge connection:
① Advantages: The connected parts can be rotated around the shaft for easy assembly and disassembly.
Structure Description: the hinge connection method includes a hinge bracket. The hinge bracket is fixed on one part by a pull nail or a screw. The other part has a hinge sleeve hole. The hinge bracket and the hinge sleeve hole are connected through the rotating shaft, and the collar holds the spindle on the bracket. prevent it from falling off.
Process design
Drawing review, to prepare the process flow of sheet metal parts, we must first know the various technical requirements of the parts drawing; The drawing review is the most important part of the design process of the part design.
1. Check whether the structure of the drawing is rigorous.
2. Whether each dimension of the drawing is clearly marked with a dimension unit.
3. The assembly relationship with the assembly steps described.
4. Translation of foreign languages.
5. Design code conversion.
6. Drawing questions and feedback.
7. Description of material list.
8. Quality requirements and process standards.
9. The formal release plan shall be affixed with the Kang Ding Quality Control Chapter.
application
With the increasing application of sheet metal processing, the requirements for sheet metal forming have become higher and higher. In fact, the overall requirements for sheet metal parts are not very high, but they pay more attention to assembly. Since the application fields of sheet metal products are very extensive, they include almost all manufacturing industries.
The main industries are communications electronics industry, automotive manufacturing, motorcycle manufacturing, aerospace industry, instrumentation industry, home appliance industry, power supply, air conditioning, power amplifiers, advertising production.
Chassis cabinet series: communication cabinets, power distribution cabinets, switch cabinets, transfer boxes, control boxes, home appliances, and other equipment.
material
The choice of materials, sheet metal, and commonly used materials are cold-rolled sheet (SPCC), hot-rolled sheet (SHCC), galvanized sheet (SECC, SGCC), copper (CU) brass, copper, beryllium copper, aluminum ( 6061, 6063, hard aluminum, etc.), Aluminum profiles, stainless steel (mirror, brushed surface, matte surface), depending on the role of different products, the choice of materials is different, generally need to consider the use of the product and cost.
1. Cold-rolled plate SPCC: mainly used for electroplating and baking paint parts, low cost, easy molding, material thickness ≤ 3.2mm.
2. Hot-rolled plate SHCC: material T ≥ 3.0mm, is also used for electroplating, paint pieces, low cost, but difficult to form, mainly used flat pieces.
3. Zinc plate SECC, SGCC: SECC plate is divided into N material and P material. N material is not used for surface treatment and the cost is high. P material is used for spraying parts.
4. Copper: The main use of conductive materials, the surface treatment is nickel, chrome, or no treatment, high cost.
5. Aluminum: General use of surface chromate (J11-A), oxidation (conductive oxidation, chemical oxidation), high cost, silver plating, nickel plating.
6. Aluminium profiles: Material parts with a complex cross-section structure are used extensively in various plug boxes. Surface treatment with aluminum plate.
7. Stainless steel: Mainly used without any surface treatment products, high cost.
Testing standards
Sheet metal quality defect description
Appearance defects
Including: cracks, necking down, deformation, pits, rust, material defects, corrugation, burrs, pulls, scratches, rounded corners, overlapping materials, and others.
2. Functional size defects
Including: hole deviation, less edges, less holes, inconsistent hole diameter, Multi material, inconsistent dimensions, and others.
3. Rework defects
Include: cracks, holes, solid inclusions, unfused and incomplete, shape defects, pits, planing marks, polishing, thinning of boards, and others.
Price calculation
There are numerous sheet metal processes. a piece of sheet metal products needs to go through many processes of many workers to complete
1, material fee: iron plate, aluminum alloy, stainless steel (Different standards of material, the price difference is much).
2. Processing fee: The production cost incurred during each process in the realization of the product, such as CNC processing fee, laser processing fee, shearing bed fee, and engraving fee, Cost of fitter, Film costs, Leveling costs, stamping costs, welding and polishing costs, bending costs, assembly costs and so on.
3, the packaging fee
4, transportation costs
5, management costs
6, profit
Surface treatment

The surface treatment of sheet metal parts is also a very important part of sheet metal processing because it has the effect of preventing parts from rusting and beautifying the appearance of the product.
The surface pretreatment of sheet metal parts is mainly used to remove oil, oxide scale, rust, etc. It prepares for surface post-treatment. Several common surface treatment methods for sheet metal are: drawbench, sandblasting, baking paint, dusting, electroplating, Anodizing, screen printing.
Equipment
Sheet metal is a comprehensive cold-working process that includes shearing, punching, cutting, compounding, folding, welding, riveting, splicing, and forming.
Basic equipment includes Shear Machine, NC Punching Machine, Laser, Plasma, Laser, Plasma, Waterjet Cutting Machine)/ Combination Machine, Bending Machine.
Various auxiliary equipment: CNC bending machine, four-column hydraulic machine, desktop tapping machine, bench drilling machine, standard exchange point (convex) welding, argon arc welding machine, uncoiler, leveling machine, deburring machine, spot welding machine, drawing machine, sandblasting machines, polishing machines, bench grinders, angle grinders, electroplating baths, oxidation bath paint lines, electrostatic powder spraying equipment, etc.
PREVIOUS:NONE
NEXT:Sheet Metal Processing Products
NEXT:Sheet Metal Processing Products









