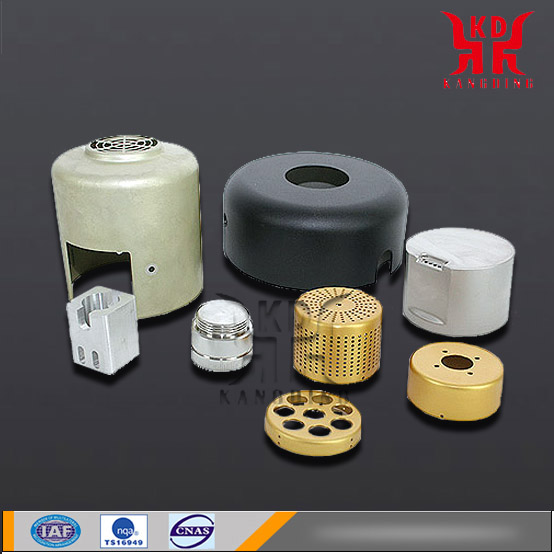
Project
Aluminium machining , using cold and hot processing methods to process aluminum billet into parts, the main methods are turning, stamping, sheet metal, rolling, extrusion, stretching and forging. Aluminium products processing, Aluminium pieces Machining, Aluminium alloy Machining, Aluminium surface treatment, Aluminium parts finishing, Aluminium shell Machining, Aluminium radiators, Aluminium bars Knurling...
Crafts
During the processing of aluminum thin-walled cavity parts, comprehensive considerations are taken into consideration in terms of optimization of process flow, heat treatment, improvement of clamping methods, and high-speed cutting processing. In combination with the structural characteristics of parts, reasonable Process flow and processing solutions are formulated.
1. The aluminum processing process can separate rough and finish machining. After rough machining is completed, heat treatment is performed on the part to fully release the cutting stress and residual stress of the part. After the finish machining, the machining quality of the part will be greatly improved. The implementation of rough and fine processing separately has the following advantages:
(1) Reduce the effect of residual stress on the deformation of aluminum processing. After the roughing is completed, the heat treatment can be used to remove the stress generated by the roughing of the part and reduce the influence of the stress on the finishing quality.
(2) Improve aluminum processing accuracy and surface quality. Coarse and fine processing are separated, and the precision machining is only a small amount of machining allowance, resulting in less processing stress and deformation, and can greatly improve the quality of parts.
(3) Improve production efficiency. Since rough machining removes only excess material and leaves a sufficient margin for finishing, it is not enough to consider dimensions and tolerances, effectively exert the performance of different types of machine tools, and improve cutting efficiency.
2.Aluminum processing heat treatment:
After the parts are cut and processed, the metal structure will undergo great changes. In addition, the effect of cutting movement will produce large residual stresses. In order to reduce the deformation of the parts, the residual stress of the materials must be fully released. Aluminum alloy thin-walled cavity parts generally use low-temperature annealing heat treatment.
3, improve the aluminum processing and clamping method:
In the processing of ordinary parts, the clamping method is usually used to set the bench vise. circular element may be employed chuck clamping manner, whether bench vise or chuck clamping fixture, will produce different degrees of clamping stress. The clamping stress and the elastic restoration after the part is removed will cause the part to have a certain deformation. In the roughing stage, because only the excess material is removed, the bench vise clamp can be used.
4, high-speed cutting aluminum processing:
During the cutting process, the main factors affecting the surface quality of the workpiece are the built-up edge of the built-up edge, the phosphatization, the vibration and the sharpening quality of the cutting edge, the defect of the workpiece material, and the use of the cutting fluid. High-speed cutting compared with ordinary cutting, cutting degree of the block, the material deformation speed, the strain rate is small, does not produce built-up edge, phosphorous thorn.
Precautions
The commonly used aluminum processing methods are: casting, cold rolling, cold drawing, cold forging, cold extrusion, stamping, etc.; in the actual production work, we also commonly encounter some aluminum alloy cutting processing such as: turning, drilling Boring, boring, milling, planing, broaching, and sawing. The aluminum material is soft and highly malleable. After machining, the aluminum parts are deformed to varying degrees due to internal stresses, cutting heat, and the influence of the fixtures. To ensure the forming quality of the parts and to control the deformation, it is necessary to handle Methods include:
(1) In the milling process, whether it is rough milling or precision milling, the part should be symmetrically processed and turned several times so that the stresses on both sides are released uniformly.
(2) When the rough machining on both sides of the part is completed, it is left for a few hours (generally 48H) so that the residual stress is fully released and then the finishing process is performed.
(3) When the part is milled on one side, try to take a small margin and multiple passes.
(4) Since the material has high strength and high toughness, it is necessary to control the depth of the knife, ensure sufficient cooling during cutting, and prevent deformation of the part due to cutting heat, and also pay attention to the hardness of the jig.
Generally, the following principles should be observed in the installation and fixture selection of aluminum workpieces:
(1) When the aluminum processing pieces are not in large quantities, combination clamps, adjustable clamps, and other universal clamps should be used as much as possible to shorten production preparation time and save production costs;
(2) Consider the use of special fixtures in batch production and strive for a simple structure;
(3) The loading and unloading of parts should be quick, convenient and reliable to shorten the pause time of the machine tool; Each component on the fixture should not interfere with the machining of the parts on the surface of the part, and the fixture can not affect the cutting in the process (such as collisions, etc.).
Aluminum alloy stamping
Aluminum alloy materials are soft, expensive, and easily broken. Some aluminum alloy products require further processing such as wire drawing and anodizing. In stamping production, it is particularly prone to produce: top injuries and scratches. Special attention must be paid to the following points in mold making:
1. For the case where the amount does not affect the project, the project at the back as far as possible punching punch. even for a product with a large number of punching holes, one more project may be considered and the punching may be ranked last.
2. The aluminum material is softer and the mold is easier to block material. Therefore, in designing the mold for clearance, a gap of 10% of the material thickness of the two sides should be placed. The straight-to-deep position of the blade is more suitable for 2 mm, and the taper is 0.8-1°.
3. During bending, aluminum chips are easily generated when the aluminum material is bent. It will cause spot injury and indentation. The aluminum raw material needs to be attached with PE film. In the case of rollers and plating, it is better to use hard chrome plating.
Surface treatment:
The surface treatment of aluminum alloy parts is divided into pre-treatment and post-treatment. The pre-treatment is to remove surface oxide skin and oil, increase post-treatment adhesion and improve the appearance effect. The most commonly used surface treatment of aluminum alloy parts are shot blasting, sandblasting and phosphating, and post-treatment is generally used for spraying, oxidation, electroplating and electrophoresis.
Choose from the cost aspect, processing methods shot blasting → blasting → phosphating → polishing, spraying → electrophoresis → oxidation → electroplating. Phosphating can only be sprayed, electrophoresed, can not do oxidation, plating.
Choose from decorative and anti-corrosion: The processing method is polishing → phosphating → sand blasting → shot blasting, oxidation → plating → spraying → electrophoresis.
1. Electrochemical method
This method is the use of an electrode reaction, the plating layer is formed on the workpiece surface. The main method is:
(1) Electroplating
In the electrolyte solution, the workpiece is the cathode. Under the action of the external current, the surface of the workpiece forms a plating layer, which is called electroplating. Coating all types of solid particles may be a metal, alloy, semiconductor, or containing, such as copper, nickel and so on.
(2) oxidation
In the electrolyte solution, the workpiece is an anode. Under the action of an external current, an oxide film layer is formed on the surface thereof, which is called anodization, and aluminum oxide film is formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy.
3, electrophoresis
The workpiece is used as an electrode, and a conductive water-soluble or water-emulsified coating is placed, and the workpiece and the other electrode in the coating constitute an electrolytic circuit. Under the action of the electric field, the coating solution has dissociated into charged resin ions, the cations move toward the cathode, and the anions move toward the anode. These charged resin ions, together with the adsorbed pigment particles, are electrophoresed onto the surface of the workpiece to form a coating. This process is called electrophoresis.

1, aluminum surface quality requirements:
| Defect name |
Defect scope
|
Value |
| Scratches |
depth(mm)
|
≤0.010 |
|
Area does not exceed the percentage of the total area
|
5 | |
| sunken | Recessed depth(mm) | ≤0.030 |
| Missing | depth(mm) | ≤0.010 |
| The length is not greater than(mm) | 2 | |
| No more than the number allowed on the surface | 2 | |
| Distance from die casting edge(mm) | ≥0.1 | |
| spacing(mm) | ≥0.2 | |
| Reticulate burrs | height(mm) | ≤0.020 |
Appearance:
1. Appearance: The surface of the oxidation part should be free of spots, blisters, pinholes, deformation, Different colors, Watermark, Mist, foreign body, Black spots, Rough, Scratches and other defects (allowing slight hanging marks to exist).
2. Characteristic test method:
1) Salt spray test: Both natural oxidation and gold oxidation salt spray tests are required to reach 168 hours (anodic oxidation 240H), and test sample results are evaluated according to QB/T 3832 standard (some companies require 100H for natural oxidation).
2) Adhesion test: Use 3M standard tape to stick. When tape is applied, the tape should be tightly bound to the test area. There should be no bubbles or wrinkles. Pull up after 2-5 minutes. No oxide film is peeled off.
3) RoHS Compliance Requirement: RoHS-compliant products are required for oxidized products; yellow oxidizers cannot yet meet environmental requirements (not universal).
Another: Anodized film thickness requirements: its thickness is 5 ~ 20 microns, hard anodized film up to 60 ~ 200 microns.
Turning
Turning of aluminum alloys falls into two categories:
Class 1 refers to industrial pure aluminum and annealed aluminum alloys with a hardness less than 80 HB;
Class 2 refers to the deformed aluminum alloy in the quenched state. The aluminum alloy turning process parameters are related to this category.
(1). Due to the relatively low strength and hardness of aluminum alloys, low plasticity, low tool wear, and high thermal conductivity, resulting in low turning temperatures, aluminum alloys have better turning performance and are easy to process materials and suitable for high speeds. Turning. But the melting point of the aluminum alloy is low, and the plasticity increases after the temperature rises. Under the action of high temperature and high pressure, the frictional force of the turning interface is very large. Easy to stick knife; especially in the annealed aluminum alloy, can not obtain a high-precision surface.
(2). Compared with steel and brass, the characteristics of aluminum alloys are 1, soft material, poor rigidity, and low elastic modulus. These two factors affect the turning processability of aluminum alloys. Therefore, when machining an aluminum alloy workpiece, it is necessary to sufficiently clamp and support the workpiece and keep the tool sharp; otherwise, the workpiece tends to leave the turning tool. Sometimes the surface of the workpiece has irregular groove marks and bright squeezing spots. One may be caused by the abnormal pressure of the tool on the workpiece, and the other may be due to chattering caused by unstable clamping. The surface of the workpiece is subjected to interstitial grinding, extrusion and powder turning; Then, when the gap or elasticity disappears, the tool bites the surface of the workpiece and marks the groove.
(3). In order to obtain a smooth workpiece surface, use a combination of rough turning and fine turning as much as possible, because a variety of qualified workpiece blanks always have some oxide layers, resulting in a considerable degree of tool wear. The above requirements can be achieved by using a sharp, polished tool for the fine turning of the final turning operation.
Technology
1. Bending
1.2.1 Using Equipment: Bending Machine
1.2.2 Technical Requirements:
1> When no size tolerance is specified, the dimensional accuracy of the workpiece after bending is controlled within 0.2mm, and the angle error is controlled within 1 degree.
2> the bend without cracks or wrinkles
3> After confirming the sample, it can be mass produced
2. Welding process
Aluminum and aluminum alloy welding methods are many, each with its own characteristics and applicable occasions. For the current structural features of Kangding's aluminum products, two welding methods, TIG welding and resistance welding, are recommended. For the aluminum and aluminum alloy welding characteristics, TIG welding and resistance welding application points and technical requirements are as follows.
2.1 TIG welding
2.1.1 Joint form and groove preparation: TIG welding Aluminium and aluminum alloy joints are: butt joints, lap joints, corner joints and T-joints. The joint geometry is similar to that of welded steel. However, due to the better fluidity of aluminum and aluminum alloys and the larger size of the torch nozzles, smaller root gaps and larger groove angles are generally used.
2.1.2 Welding current types
The use of alternating current welding of aluminum and aluminum alloys achieves good purification while at the same time achieving a satisfactory penetration depth. If a pulsed current is used, the arc energy can be precisely controlled and the control of the weld pool can be achieved, which is advantageous for thin plates or all-position welding.
2.1.3 welding process points
TIG welding is suitable for welding aluminum and its alloys with a thickness of less than 12mm. when the thickness is less than 3mm, single-pass welding is generally used on steel pads. When the thickness is 4 to 6 mm, it is usually welded by double-sided welding. when the thickness is larger than 6mm, shall beveling.
PREVIOUS:NONE
NEXT:CNC Machining Custom Heatsink
NEXT:CNC Machining Custom Heatsink